When a stroke occurs, time is brain. Clinicians need fast, accurate information to determine the best treatment. This is where StrokeViewer’s CT Perfusion (CTP) algorithm makes a difference: turning raw imaging data into actionable insights that support time-critical decisions.
What Is CT Perfusion?
CTP is an advanced diagnostic imaging technique that assesses blood flow through tissue. It’s commonly used to examine the brain, heart, liver, and other organs, where understanding blood supply is crucial. In stroke care, CTP helps clinicians identify which brain tissue is already irreversibly damaged (the core) and which tissue is at risk but still salvageable (the penumbra).
This distinction is vital. CTP plays a key role in identifying the late-window (6-24 hours after symptom onset) stroke patients who may still benefit from thrombectomy. Clinical trials like DAWN and DEFUSE 3 have shown that CTP can safely expand treatment eligibility for patients once considered untreatable.
Supporting Critical Decisions in Stroke Triage
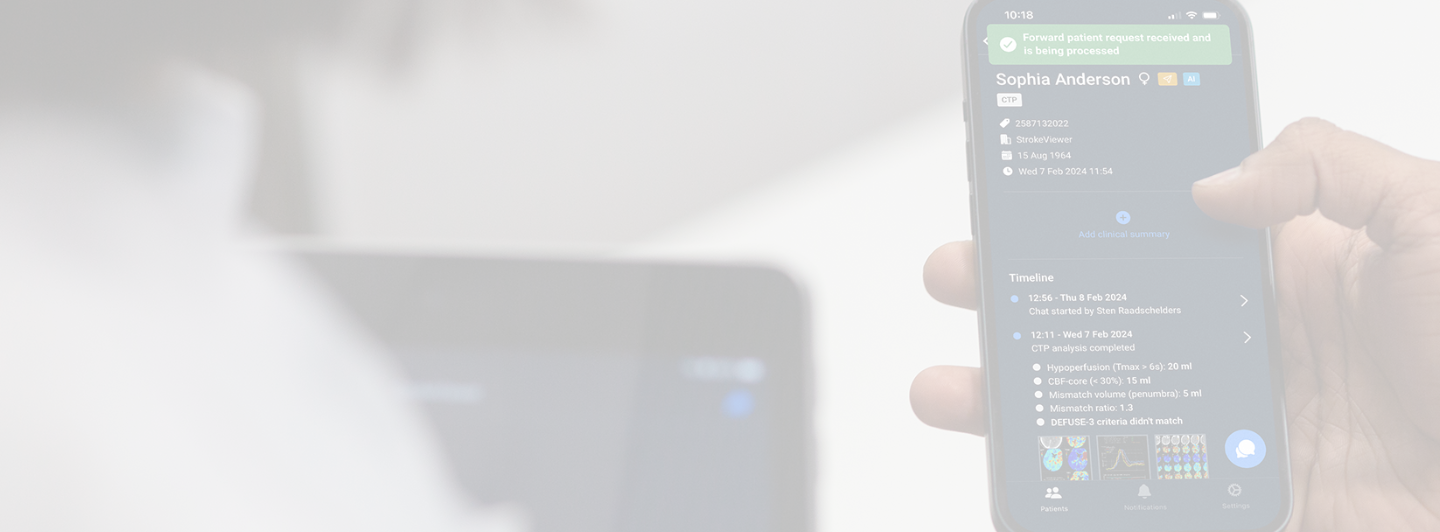
One of the most important factors in stroke triage is the mismatch ratio: The volume of salvageable tissue compared to the infarcted core. Thrombectomy eligibility depends not only on how much tissue is lost but how much can still be saved.
CTP remains the only imaging modality that estimates core and penumbra based on real-time blood flow. StrokeViewer’s algorithm takes it a step further. It quantifies both salvageable and infarcted tissue, providing data that guides treatment decisions.
Transparent AI You Can Trust
StrokeViewer is designed for transparency: it not only displays the final output (such as the calculated core and penumbra volumes) but also the underlying data and processing steps. This includes access to:
- perfusion maps
- Tmax thresholds
- Time–intensity curves
- Segmentation boundaries.
By making the algorithm’s logic visible, StrokeViewer enables clinicians to validate the findings, interpret results in context, and build trust in AI-assisted decisions.
Inside StrokeViewer’s CTP Analysis: Key Outputs Explained
Our CTP algorithm analyses time-based contrast enhancement in the brain and generates intuitive and easy-to-read perfusion maps. These maps reflect:
- TMax (Time to Maximum Contrast Enhancement): Highlights delayed blood flow, where values over 6 seconds may indicate ischemia.
- CBF (Cerebral Blood Flow): Measures the rate of blood flow per second, compared with the healthy brain regions, shown as a percentage.
- CBV (Cerebral Blood Volume): Represents the total volume of blood in a given brain area, shown as a percentage.
- Lesion Map: Using validated DEFUSE 3 thresholds, StrokeViewer automatically identifies and quantifies core and penumbra volumes in milliliters.
What’s New: Continuous Innovation Based on User Feedback
At Nicolab we are committed to continuous innovation. Based on customers’ feedback, we keep refining our algorithm to enhance clinical value. Recent updates include:
- Sharper perfusion maps with refined time sampling and more accurate Tmax values.
- Improved colour range: Expanded CBF/CBV colour range (0-200%) for improved visual interpretation.
- New segmentation algorithm for clearer anatomical definition and fewer artefacts.
- Image downsampling has been refined to better preserve clarity and resolution, ensuring high-quality visual outputs while maintaining processing efficiency.
- Improved temporal processing for greater consistency across different acquisition schemes.
Limitations, Considerations and Alterations
Like any medical technology, CTP has limitations. It’s operator-dependent, sensitive to patient motion, and carries a higher radiation dose than some alternatives. There’s also the risk of ghost cores (falsely large core estimates) or false positives on the penumbra.
Moreover, CTP isn’t available in every hospital and can be time and resource-intensive.
Despite these challenges, it remains a valuable tool, especially as stroke care evolves towards more personalised treatment and improved occlusion detection. Trends suggest a shift toward simpler or biomarker-based triage tools. However, the push for M2 occlusion detection and personalised treatment models means CTP still has an important role. Nicolab brings the CTP algorithm and rapid communication on one intuitive platform.
Conclusion: StrokeViewer’s CTP Empowers Faster Stroke Decisions
As late-window thrombectomies become more common, StrokeViewer’s CTP algorithm delivers fast, reliable insights. It helps clinicians make smarter, more confident decisions when time matters most.